Foundation Flaws: What Your Brick Walls Are Trying to Tell You

Foundation Flaws are a serious concern for homeowners and building owners alike, as they can compromise the structural integrity of a property. In this article, we’ll delve into the telltale signs of foundation damage in brick structures, arming you with the knowledge to identify potential issues early on. By understanding these signs, you can take proactive steps to address any problems before they escalate, ultimately safeguarding your investment and ensuring the longevity of your brick-built home or commercial establishment.
Brick structures are renowned for their durability and timeless appeal, but even these sturdy edifices can succumb to the effects of Foundation Flaws over time. From cracked bricks to uneven floors and walls, we’ll explore the common indicators that something may be amiss with your foundation. By recognizing these warning signs early, you can mitigate the risk of costlier repairs and potential safety hazards down the line.
Understanding Foundation Damage
Foundation damage refers to the deterioration or shifting of a building’s foundation, which is the underlying structure that supports the entire weight of the construction above. This damage can occur gradually over time due to various factors, such as soil movement, excessive moisture, or poor construction practices. When a foundation becomes compromised, it can lead to structural issues throughout the property, potentially causing cracks, uneven settling, and even complete failure in severe cases.
Early detection of Foundation Flaws is crucial, as addressing issues in their initial stages can often be more cost-effective and less disruptive than tackling advanced problems. Prompt intervention can prevent further deterioration and ensure the structural integrity of your brick structure for years to come.
Early Signs of Foundation Damage
Cracked Bricks
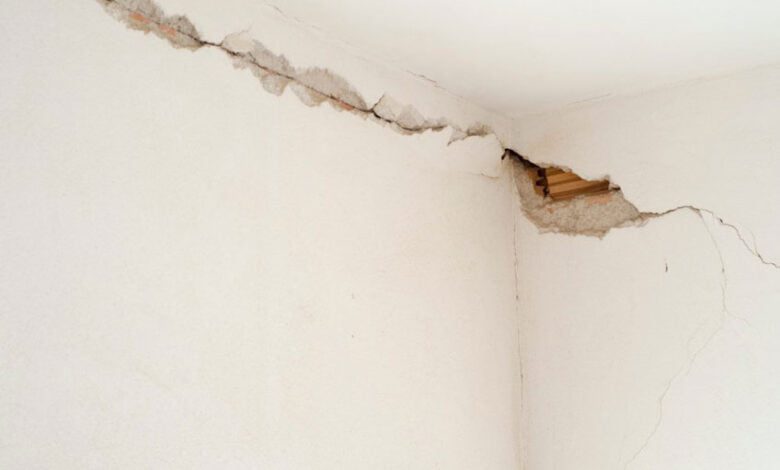
One of the most visible and telltale signs of foundation damage in brick structures is the appearance of cracked bricks. These cracks can manifest in various patterns and locations, ranging from hairline fractures to larger, more pronounced splits. While not all cracks necessarily indicate foundation issues, they can be a warning sign that should not be ignored.
Cracked bricks can occur due to the shifting or settling of the foundation, which exerts uneven pressure on the brickwork. These cracks may appear around windows, doors, or along the corners of the structure, as these areas are particularly susceptible to the effects of foundation movement. Additionally, cracks that run diagonally or vertically through multiple bricks can be a significant cause for concern, as they may indicate more severe foundation problems.
Uneven Floors and Walls
Another early indicator of Foundation Flaws in brick buildings is the presence of uneven floors and walls. As the foundation shifts or settles unevenly, it can cause the floors to slope or sag, and walls to lean or become misaligned. This unevenness can be visually apparent or felt when walking across the affected areas.
Uneven floors can be particularly noticeable in hallways or larger open spaces, where even slight variations in the level become more pronounced. Similarly, walls that appear to be leaning or bowing can be a clear sign that the foundation underneath is experiencing issues.
Note that some minor unevenness may be expected in older structures due to natural settling over time. However, investigate significant or widespread unevenness promptly, as it could indicate more serious foundation problems.
Major Indicators of Foundation Damage
While the early signs mentioned above warrant attention, there are more severe indicators that suggest advanced foundation damage in brick structures. These major signs should be addressed as a matter of urgency to prevent further deterioration and potential structural failures.
Bulging or Bowing Walls
One of the most concerning signs of foundation damage is the presence of bulging or bowing walls. This occurs when the foundation shifts or settles unevenly, causing the walls to bow inward or outward in response to the uneven pressure exerted on the structure.
Bulging or bowing walls can be a clear indication that the foundation is experiencing significant issues, such as soil erosion, excessive moisture, or structural overload. These walls may appear curved or distorted, and in severe cases, cracks or separations may form along the bulging areas.
Doors and Windows that Stick or Won’t Close Properly
Another major indicator of Foundation Flaws is when doors and windows become difficult to open or close properly. This issue can arise due to the shifting or settling of the foundation, which can cause the frames of these openings to become misaligned or distorted.
If you notice that doors and windows are sticking, rubbing against their frames, or refusing to close properly, it could be a sign that the foundation has shifted, causing the structural elements to move out of alignment. This issue should not be ignored, as it can lead to further damage and potential safety hazards if left unaddressed.
The Role of Water in Foundation Flaws
Water is one of the most significant contributors to foundation damage in brick structures. Excessive moisture, whether from poor drainage, leaks, or high water tables, can wreak havoc on foundations over time.
When water accumulates around the foundation, it can cause the soil to expand or contract, leading to uneven settling and pressure on the structure. Additionally, prolonged exposure to moisture can cause the foundation materials to deteriorate, weakening their ability to support the weight of the building above.
How Water Contributes to Foundation Flaws
Water can contribute to foundation damage in several ways:
- Soil Erosion: Excessive water flow or poor drainage can wash away soil from around the foundation, undermining its support and stability.
- Hydrostatic Pressure: High water tables or saturated soil can exert significant hydrostatic pressure on the foundation, causing it to crack, shift, or bow.
- Soil Expansion and Contraction: When clay-rich soils become saturated with water, they can expand, putting immense pressure on the foundation. Conversely, during dry periods, these soils can contract, leading to settlement and cracking.
- Deterioration of Materials: Prolonged exposure to moisture can cause the deterioration of concrete, steel, and other foundation materials, compromising their structural integrity over time.
Inspecting Brickwork for Damage
While some signs of Foundation Flaws may be visually apparent, a thorough inspection of the brickwork is essential to identify any potential issues. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to inspect your brick structure for signs of damage:
- Start from the Ground Up: Begin your inspection by examining the foundation itself. Look for cracks, bulges, or signs of water intrusion near the base of the structure.
- Inspect the Exterior Walls: Carefully examine the exterior brick walls for any visible cracks, discoloration, or unevenness. Pay close attention to areas around windows, doors, and corners, as these are common spots for stress points and cracks to appear.
- Check Window and Door Frames: As mentioned earlier, windows and doors that stick or won’t close properly can indicate signs of foundation issues. Inspect these areas for any misalignment or gaps between the frames and the surrounding brickwork.
- Look for Stair-Step Cracks: Stair-step cracks, which resemble a series of steps or a zigzag pattern, are often a telltale sign of foundation settlement or movement.
- Examine the Interior Walls: Don’t forget to inspect the interior walls for any cracks, bulges, or unevenness. These signs can also indicate potential foundation problems, even if the exterior brickwork appears intact.
- Assess the Floors: Walk across the floors, paying attention to any noticeable slopes, dips, or unevenness. These can be indications of foundation settlement or shifting.
As you inspect your brick structure, it’s essential to document any potential issues you find. Take photographs, make notes, and mark the locations of any cracks or damage you observe. This documentation will be invaluable if you need to consult with a professional or seek repairs in the future.
Common Signs of Foundation Damage
| Sign of Damage | Potential Implications |
|---|---|
| Cracked Bricks | Foundation shifting or settling, uneven pressure on brickwork |
| Uneven Floors and Walls | Foundation settlement, soil movement, structural issues |
| Bulging or Bowing Walls | Significant foundation issues, soil erosion, structural overload |
| Doors and Windows Sticking | Foundation shifting, misaligned frames |
| Water Intrusion or Moisture | Potential for soil erosion, hydrostatic pressure, material deterioration |
| Stair-Step Cracks | Foundation settlement or movement |
Causes of Foundation Flaws in Brick Structures
Foundation damage in brick structures can arise from various natural and man-made causes. Understanding these causes is crucial in identifying potential risks and taking preventative measures.
Natural Causes
- Soil Movement: One of the primary natural causes of foundation damage is soil movement. This can occur due to factors such as expansive clay soils, which expand and contract based on moisture levels, or soil erosion caused by water flow or improper drainage.
- Weather Conditions: Extreme weather conditions, such as prolonged drought or heavy rainfall, can contribute to soil movement and put stress on the foundation. Temperature fluctuations can also cause materials to expand and contract, leading to cracks and fissures.
- Tree Roots: The growth of tree roots near a foundation can exert significant pressure on the structure, potentially causing cracks or shifting as the roots expand and seek moisture.
- Earthquakes and Seismic Activity: In areas prone to earthquakes or seismic activity, the ground movement can cause foundation damage, cracking, and structural issues in brick buildings.
Man-made Causes
- Poor Construction Practices: Inadequate site preparation, improper foundation design, or substandard construction materials can lead to foundation problems from the outset. Even minor deviations from building codes and best practices can have long-term consequences.
- Inadequate Drainage Systems: Poorly designed or maintained drainage systems can allow water to accumulate around the foundation, leading to soil erosion, hydrostatic pressure, and potential foundation damage.
- Nearby Construction Activities: Excavation or construction projects near a brick structure can cause vibrations, soil disturbance, or changes in water flow patterns, all of which can impact the foundation.
- Overloading: Adding excessive weight or load-bearing structures to a brick building without properly reinforcing the foundation can lead to structural issues and potential foundation failure.
By understanding these natural and man-made causes, homeowners and building owners can take proactive measures to mitigate risks and address any potential issues before they escalate into more severe foundation damage.
Repair Solutions for Foundation Damage
If you suspect or have identified foundation damage in your brick structure, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly. Ignoring foundation problems can lead to further deterioration, potential safety hazards, and significantly higher repair costs in the long run.
Overview of Repair Methods
The appropriate repair method for foundation damage will depend on the severity and extent of the issue, as well as the underlying cause. Here are some common repair solutions:
- Underpinning: This process involves reinforcing or extending the existing foundation by installing additional support structures, such as concrete piers or piles, beneath the affected areas.
- Foundation Piering: Similar to underpinning, piering involves installing steel or concrete piers beneath the foundation to provide additional support and stabilize the structure.
- Slab Jacking or Mudjacking: For minor settling or unevenness, slab jacking or mud jacking techniques can be used to raise and level the concrete slab or foundation by injecting a grout mixture beneath it.
- Crack Repair: Smaller cracks in the foundation or brickwork can be repaired using specialized epoxy or polyurethane injection methods, which help seal and stabilize the cracks.
- Foundation Replacement: In cases of severe or widespread damage, partial or complete foundation replacement may be necessary. This is typically the most expensive and invasive option but may be unavoidable in certain situations.
When to DIY and When to Call a Professional
Some minor foundation repairs, such as sealing small cracks or addressing minor drainage issues, may be suitable for the handy homeowner. However, it’s important to recognize the limitations of DIY projects and when professional assistance is required.
If you suspect significant foundation damage, such as bulging walls, severe cracking, or widespread settling, it’s advisable to consult with a structural engineer or foundation repair specialist. These professionals have the expertise and equipment necessary to properly assess the extent of the damage and recommend the most appropriate repair solution.
Attempting major foundation repairs without professional guidance and experience can lead to further issues, compromised safety, and potentially costly mistakes. In such cases, entrust the work to qualified professionals who can ensure they properly restore the structural integrity of your brick structure.
Preventing Foundation Flaws in Brickworks
While repairing existing Foundation Flaws is essential, prevention is often the most effective and cost-efficient approach. By taking proactive measures and implementing regular maintenance practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of foundation issues in your brick structure.
Tips for Maintenance and Prevention
- Ensure Proper Drainage: Maintain a well-functioning drainage system around your property, including properly graded landscapes, clear gutters and downspouts, and adequate drainage channels to divert water away from the foundation.
- Monitor Soil Conditions: Be aware of the soil conditions surrounding your brick structure. If you have expansive clay soils, consider implementing strategies to minimize moisture fluctuations, such as installing root barriers or adjusting your irrigation practices.
- Trim Nearby Trees and Shrubs: Regularly trim trees and shrubs whose roots could potentially encroach on the foundation area. This helps prevent root growth from exerting pressure on the structure.
- Conduct Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect your brick structure for any signs of cracks, unevenness, or other potential issues. Early detection can help prevent further damage and facilitate prompt repair.
- Address Minor Issues Promptly: If you notice any minor cracks, settling, or other signs of potential foundation damage, don’t hesitate to address them promptly. Small issues can often be resolved before they escalate into more significant problems.
- Consider Professional Assessments: Periodically, consider hiring a professional structural engineer or foundation repair specialist to conduct a comprehensive assessment of your brick structure. Their trained eye and expertise can identify potential issues that may not be readily apparent to the untrained eye.
Importance of Regular Inspections and Early Intervention
Regular inspections and early intervention are crucial in preventing foundation damage from worsening. By monitoring your brick structure closely and addressing issues as soon as they arise, you can minimize the extent of the damage and the associated repair costs.
Furthermore, addressing foundation problems early can help prevent secondary issues from developing, such as cracked interior walls, stuck doors, and windows, or even structural failures in extreme cases. Early intervention not only saves you money in the long run but also ensures the safety and longevity of your brick structure.
The Impact of Foundation Damage on Property Value
Foundation Flaws can have a significant impact on the resale value of a property, making it a concern not only for the current homeowner or building owner but also for potential buyers.
When foundation issues are present, prospective buyers may be hesitant to proceed with a purchase due to the potential costs and hassle associated with repairing the damage. Even if repairs have been made, buyers may be wary of the long-term implications and the possibility of unaddressed or recurring issues.
Additionally, many lenders and mortgage companies may require a structural inspection or engineering report before approving financing for a property with known foundation damage. This added scrutiny and potential for additional costs can further complicate the selling process.
Address foundation damage promptly and thoroughly to mitigate the negative impact on your property’s value. Documented repairs and maintenance records can assure potential buyers that you have appropriately addressed the issues, increasing the likelihood of a successful sale at a fair market value.
On the other hand, if you ignore or attempt to conceal foundation damage, you can face severe consequences. Not only do you jeopardize the structural integrity of the property, but you can also incur legal liabilities if you do not properly disclose the issues during the selling process.
Before and After Foundation Repair
To better illustrate the impact of Foundation Flaws and the potential for successful repairs, let’s explore a few real-life case studies.
Case Study 1:
Before Repair: A century-old brick home in a residential neighborhood was experiencing significant foundation settlement issues. Cracks had formed throughout the exterior brickwork, walls were visibly bowing, and doors and windows were sticking or unable to close properly. The homeowners had noticed these signs for years but had neglected to address them promptly.
Repair Process: After consulting with a structural engineer, it was determined that the foundation had settled unevenly due to expansive clay soils and inadequate drainage around the property. The recommended repair solution involved underpinning the entire foundation using concrete piers driven deep into stable soil layers.
This process required excavation around the perimeter of the home, installation of the piers, and careful lifting and stabilization of the structure. Additionally, the drainage system was improved, and the exterior brickwork was repaired or replaced where necessary.
After Repair: The underpinning and drainage improvements successfully stabilized the foundation, and the home was leveled and secured. The brickwork was repaired, and the doors and windows once again operated smoothly. The homeowners reported a significant improvement in the structural integrity and overall appearance of their property.
Case Study 2:
Before Repair: A two-story brick building housing a restaurant and retail space was experiencing cracks in the foundation and exterior walls. These cracks were initially small but had gradually worsened over time, prompting concerns about the structural safety of the building.
Repair Process: An evaluation by a foundation repair specialist revealed that the cracks were caused by a combination of soil movement and poor drainage around the building. The recommended solution involved injecting polyurethane foam into the cracks to seal and stabilize them, followed by the installation of a comprehensive drainage system to divert water away from the foundation.
After Repair: The polyurethane injection successfully sealed the cracks, preventing further water intrusion and soil movement. The new drainage system addressed the underlying moisture issues, reducing the risk of future foundation damage. The foundation repair company restored the building’s structural integrity, allowing the commercial tenants to continue operating their businesses without interruption.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations for Homeowners
These case studies highlight the importance of addressing foundation damage promptly and seeking professional expertise. Ignoring the early signs of damage can lead to more severe and costly issues down the line, as seen in the first case study.
For homeowners, it’s crucial to conduct regular inspections of their brick structures and be attentive to any potential signs of foundation damage. If issues are identified, it’s advisable to consult with a qualified professional for an accurate assessment and recommended course of action.
Additionally, implementing preventative measures, such as maintaining proper drainage systems and addressing soil conditions, can go a long way in minimizing the risk of foundation damage from the outset.
By taking a proactive approach and addressing issues promptly, homeowners can protect the structural integrity and value of their brick properties, ensuring their longevity for years to come.
Conclusion
Foundation damage in brick structures is a serious concern that should not be overlooked. By recognizing the telltale signs, such as cracked bricks, uneven floors and walls, bulging or bowing walls, and doors and windows that stick or won’t close properly, you can take proactive steps to address any potential issues before they escalate.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the various causes of foundation damage, both natural and man-made, and emphasized the importance of early detection and intervention. We’ve also delved into the role of water in contributing to foundation problems and highlighted preventative measures to mitigate water-induced damage.
From inspecting brickwork for signs of damage to understanding the implications of different repair methods, this comprehensive guide has armed you with the knowledge necessary to tackle foundation issues head-on.
Remember, addressing foundation damage promptly not only safeguards the structural integrity of your brick structure but also protects your investment and property value. By taking proactive steps in maintaining and repairing foundations, you can ensure the longevity of your brick-built property for generations to come.
Don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance when needed, as foundation repairs can be complex and require specialized expertise. With the right knowledge and approach, you can confidently navigate the challenges of foundation damage and preserve the beauty and durability of your beloved brick structure.